[C Question] 더블 포인터와 구조체
카테고리: c-question-lv1
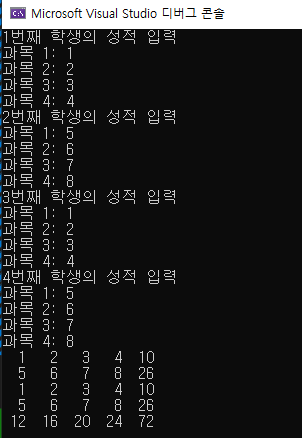
1. 과목과 총점구하기 ( 전역 변수 )
#include <stdio.h>
int record[5][5];
void writeRecord();
void writeSumRecord();
void showAllRecord();
int main()
{
writeRecord(); // 입력
writeSumRecord(); // 총점 구하는 함수 ( 9칸 )
showAllRecord(); // 값을 보여줌
return 0;
}
조건 : main은 어떤 것도 건드려서는 안 된다 !
정답
2. 더블 포인터의 활용
#include <stdio.h>
void MaxAndMin(int* arr, int len, int** maxPtr, int** minPtr);
int main()
{
/* 연습문제
다음과 같이 두개의 int형 포인터 변수와 길이가 5인 int형 배열을 선언한다.
그리고 MaxAndMin이란 이름의 함수를 정의
호출하면서 두 포인터 변수에 대한 정보를 전달
어떠한 정보를 어떻게 전달할지는 스스로 결정
함수 호출이 완료되면, 포인터 변수 maxPtr에는 가장 큰 값이 저장된
배열요소의 주소 값!!!이,
minPtr에는 가장 작은 값이 저장된 배열 요소의 주소 값!!!!이 저장됨.
*/
int* maxPtr;
int* minPtr;
int arr[5];
int i, len;
len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
// 배열에 값 입력
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
printf("정수 입력 %d : ", i + 1);
scanf_s("%d", &arr[i]);
}
// 함수 호출
// 출력
printf("최대: %d, 최소: %d", *maxPtr, *minPtr);
return 0;
}
조건
메인 5줄 ( 변수 빼고 )
함수 6줄
정답
3. 직원 구조체
#include <stdio.h>
struct employee
{
char name[50];
char addr_num[15];
int salary;
};
int main()
{
/* 연습문제
문자열 형태의 종업원 이름과 주민등록번호
그리고 정수 형태의 급여정보를 저장할 수 있는 employee라는 이름의 구조체 정의
구조체 변수를 하나 선언한 다음 사용자 입력받아서 변수를 채우고,
구조체 변수에 채워진 데이터를 출력한다.
*/
struct employee salary_info;
// 입력
// 출력
printf("--- 종합 정보--- \n\n이름: %s \n주민등록번호: %s \n월급은?: %d", salary_info.name, salary_info.addr_num, salary_info.salary);
return 0;
}
댓글 남기기